Mr. Yankey's World History
This is a great resource for maps
BBC Indus Valley interactive site
Great interactive resources for Ancient Indus Valley
A homeschool resource website aimed to not only show what we are learning about but allow others to share in our learning through posts, links and video. We believe that curiosity and creativity should be the main engines through which learning takes place. We incorporate character building activities throughout our homeschool process.
Monday, November 17, 2014
Wednesday, August 6, 2014
Thursday, July 3, 2014
Thursday, June 5, 2014
Saturday, May 24, 2014
Henri Rousseau
Youtube - Jungle Print
Incredible Art.org

Henri Rousseau's work
Henri Rousseau documentary - Youtube
Sunday, May 18, 2014
Friday, May 2, 2014
Little artist
Paint, Draw and Create. Allow your children to do the same.
Kids Artist Blogspot
Teach Kids art
Kinder art
http://www.goshen.edu/art/ed/draw.html
Artist Birthdays
teaching Ideas
Kids Artist Blogspot
Teach Kids art
Kinder art
http://www.goshen.edu/art/ed/draw.html
Artist Birthdays
teaching Ideas
Beginning Piano
I was reminded over the weekend of the importance of music for young minds. I've taken for granted how much music is a part of life. Because of this we are incorporating music and piano lessons into our regular studies.
But we need to start at the beginning. One of my children has a lot of experience with the viola and French Horn but has no Piano experience. My second son is very musically inclined and took lessons for about a year and my two youngest have no experience at all. So we all are at different levels.
Music matters blog
Piano Pronto
Opus Music Worksheets
But we need to start at the beginning. One of my children has a lot of experience with the viola and French Horn but has no Piano experience. My second son is very musically inclined and took lessons for about a year and my two youngest have no experience at all. So we all are at different levels.
Music matters blog
Piano Pronto
Opus Music Worksheets
Sunday, April 27, 2014
Tuesday, April 22, 2014
Bees Bees
This week Bee wanted to teach about Bee's. This is very interesting
Here are some things we will be doing
Bee's making honey out of nectar
We are also talking about pollination

Here are some things we will be doing
Bee's making honey out of nectar
We are also talking about pollination

Thursday, April 10, 2014
Friday, March 7, 2014
Miss Mee's Clownfish
The study of anemonefish is a perfect setting to introduce the idea of symbiosis. Even small children can understand long-term interactions between different species that are mutually beneficial. There are so many instances in nature where this occurs the anemonefish is just one example. For my older children Mee will give them the challenge of finding two more examples of symbiosis in nature.
kidzworld.com

symbiosis video

Learn to draw a clownfish
kidzworld.com
symbiosis video
Learn to draw a clownfish
Plymouth Colony

History.com
Plymouth's government was initially vested in a body of freemen who met in an annual General Court to elect the governor and assistants, enact laws, and levy taxes. By 1639, however, expansion of the colony necessitated replacing the yearly assembly of freemen with a representative body of deputies elected annually by the seven towns. The governor and his assistants, still elected annually by the freemen, had no veto. At first, ownership of property was not required for voting, but freemanship was restricted to adult Protestant males of good character. Quakers were denied the ballot in 1659; church membership was required for freemen in 1668 and, a year later, the ownership of a small amount of property as well.
Plymouth was made part of the Dominion of New England in 1686. When the Dominion was overthrown (1689), Plymouth reestablished its government, but in 1691 it was joined to the much more populous and prosperous colony of Massachusetts Bay to form the royal province of Massachusetts. At the time Plymouth Colony had between 7,000 and 7,500 inhabitants.
Oscar Zeichner
Bibliography: Adams, J. T., The Founding of New England (1921; repr. 1963); Bradford, William, Of Plymouth Plantation, 1620–1647, ed. by S. E. Morison (1952); Deetz, James and Patricia Scott, The Times of Their Lives: Life, Love and Death in Plymouth Colony (2000); Demos, John, A Little Commonwealth — Family Life in Plymouth Colony (1988); Langdon, G. D., Jr., Pilgrim Colony (1966); Morison, S. E., The Story of the Old Colony of New Plymouth (1956); Smith, Bradford, Bradford of Plymouth (1951); Stratton, E. A., Plymouth Colony: Its History and People (1987).
(From scholastic.com)
plymouth colony powerpoint
FOR THE YOUNGER KIDS

reenactment
Thursday, February 20, 2014
Bee's Squid
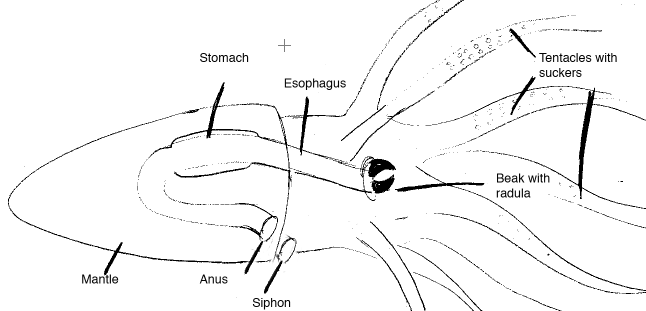
This week Bee is teaching us about squids. She has a lot of fun things planned for us. I will be helping her with some of these lessons. We will start off by talking about the importance of working as a team and taking different scientific approaches for a common goal.
Squid Dissection - We used this as a guide to our dissection
After we identified the organs, the pen and the beak as well as the sex of our squid, we cleaned them and fried them up.
http://www.discovery.com/tv-shows/curiosity/videos/the-giant-squid-discoverers.htm
"The giant squid discoverers" at discovery.com explains a wonderful approach to solving scientific problems and working on research as a team.
Giant squid
Squid experiment - almost unschoolers

origami squid
Tree of Life
CBS News - Hombolt Squid

winky the homboldt squid

Squid Dissection - We used this as a guide to our dissection
After we identified the organs, the pen and the beak as well as the sex of our squid, we cleaned them and fried them up.
We fried them up in butter, garlic, and onion. I thought they were rather tasty but the kids thought they were a little fishy. Imagine that.
Bee liked them the most. She chowed down and finished off several of them
http://www.discovery.com/tv-shows/curiosity/videos/the-giant-squid-discoverers.htm
"The giant squid discoverers" at discovery.com explains a wonderful approach to solving scientific problems and working on research as a team.
Giant squid
Squid experiment - almost unschoolers

origami squid
Tree of Life

CBS News - Hombolt Squid

winky the homboldt squid
Coffee filter squid
 |
| We took two coffee filters and put a little stuffing between two and stapled them together |
 |
| Then we made tentacles and arms by cutting strips out of another filter and stapled them on the bottom and painted them with watercolor. |
 |
| In the end we made a squid wall to display our little critters |
 |
| We also created salt dough squid and baked them |

Sunday, February 2, 2014
Early American Explorers 1535-1543
Monday


- 1535 - Jacques Cartier travels up the St. Lawrence River to Quebec and Montreal.
biography clip
- 1539 - Fray Marcos de Niza searches for the Seven Cities of Gold and wanders over New Mexico.

Wednesday
1539-41 - Hernando de Soto explores Florida, Georgia, and Alabama, and becomes the first European to cross the Mississippi River.

1540-42 - Francisco Vásquez de Coronado explores the Gila River,
the Rio Grande, and the Colorado River. He reaches as far north as
Kansas before returning to Mexico City. He too searches for the
legendary Seven Cities of Gold.


Friday
1542 - Juan Rodriguez Cabrillo sails up the California Coast and claims it for Spain.


1543 - Followers of Hernando De Soto sail from the Mississippi River to Mexico.
Bartolome Ferrelo continues sailing north up California and reaches what is probably present day Oregon.
Bartolome Ferrelo continues sailing north up California and reaches what is probably present day Oregon.
Sea Turtles
As part of our ocean studies we are learning about sea turtle. Living so close to a beach that has turtle nesting for a good part of the year is a trip. It's one thing to read about turtles nesting but to see the actual nests and turtle prints is another. I'm looking forward to this summer. I really hope that we can see turtle prints and hopefully even a nest site.
Monday
Folly Beach Turtle Watch Program

Pamela Susan Turtle poem and pet

Wednesday

Sea Turtle Documentary
This is a fascinating documentary about Leather Back Turtles. I had no idea how amazing their anatomy is. It does show a dissection of a Leather Back Turtle that was killed by a boat propeller and does talk quite extensively about its sex organs(which I will edit for my children) but very informational. Two thumbs up
Easy oragami turtle

Friday

Sea Turtle Conservancy

We will also be watching this on netflix.


Monday
Folly Beach Turtle Watch Program

Pamela Susan Turtle poem and pet
Wednesday

Sea Turtle Documentary
This is a fascinating documentary about Leather Back Turtles. I had no idea how amazing their anatomy is. It does show a dissection of a Leather Back Turtle that was killed by a boat propeller and does talk quite extensively about its sex organs(which I will edit for my children) but very informational. Two thumbs up
Easy oragami turtle

Friday

Sea Turtle Conservancy
We will also be watching this on netflix.


Sunday, January 26, 2014
Bee's Birds
Last week we did a trial run of letting the kids teach a science subject. It was such a hit we are going to continue. The conditions are that they must study the subject out. For the younger kids that includes reading a book and reading several other sources. For the older kids this can include a deeper look into a subject. I have allowed each child a day or two to present their lesson along with projects or experiments that go along with it.
Monday we are starting with our youngest. She will need lots of assistance in her lesson so we will link some of the information that we find here. After reading a book about birds she was so excited to teach the fam everything the learned.
www.allaboutbirds.org

This is a fun sight that allows you to identify birds. It also has a lot of wonderful ideas for getting out and star identifying birds in your area. It also has life history, video and bird calls.
Junior bird list
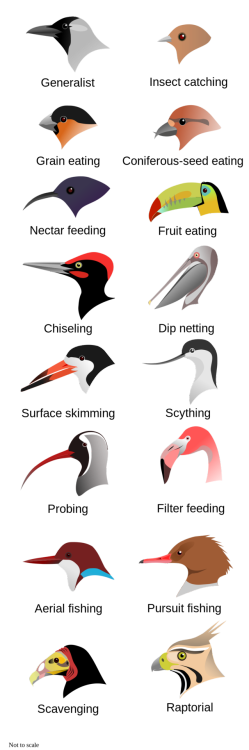
Types of beaks
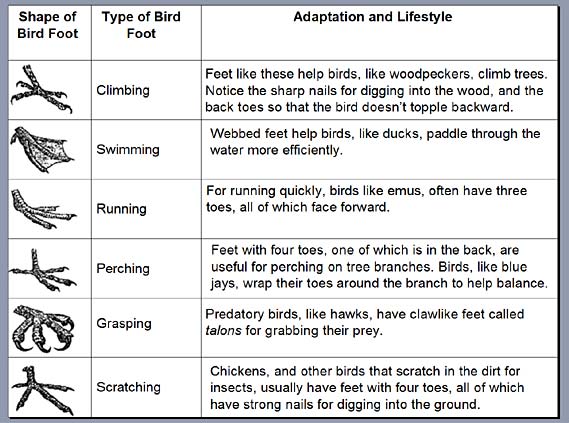
Types of bird feet
Parts of the birds

bird crafts
oragami bird

Monday we are starting with our youngest. She will need lots of assistance in her lesson so we will link some of the information that we find here. After reading a book about birds she was so excited to teach the fam everything the learned.
www.allaboutbirds.org

This is a fun sight that allows you to identify birds. It also has a lot of wonderful ideas for getting out and star identifying birds in your area. It also has life history, video and bird calls.
Junior bird list
Types of beaks

Types of bird feet

Parts of the birds

bird crafts
oragami bird
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)











